Androgenetic alopecia is a type of non-scarring hair loss commonly referred to as male or female pattern baldness. It’s the most common type of hair loss in men and women worldwide. In androgenetic alopecia, the hair follicle is not destroyed and have a better chance of being reversed than scarring types of hair loss. Although this form is called “male pattern baldness”, androgenic alopecia can also affect women and is the most common form (50% of cases).
Androgenetic alopecia involves the existence of an abnormal gene passed on at birth. Androgenic alopecia can be inherited from either or both parents. This abnormal gene has not yet been identified despite extensive scientific research.
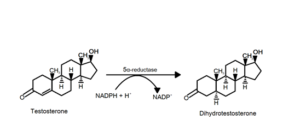
Thanks to modern research on the genetics and chemistry of male hormones, we know that the pathological basis of androgenetic alopecia is the result of male hormones – testosterone and dihydrotestosterone (DHT) – on genetically predisposed individuals.
DHT attaches to androgen receptors in the dermal papilla and tissues around the hair follicles. Hair follicles of individuals prone to androgenic alopecia become sensitive to DHT and start to shrink, resulting in hair thinning. Other conditions can also affect hormones and result in non-scarring hair loss such as polycystic ovarian syndrome and hypothyroidism.
Androgenetic hair loss is “chronic” and “progressive:” It is well documented that men who are subject to hair loss will continue to lose more hair if the condition is not treated and stabilized. It is characterized by a progressive decrease in the quantity and quality of hair that very often begins in adolescence.
- A miniaturization of the follicle occurs: the hair becomes sparse, thin and only slightly longer.
- The root begins to shrink and the hair growth cycle is reduced.
- A thinning process of the hair that gradually becomes down.
- Eventually, the hair root dies and at this point it is too late to intervene.
It is generally faster and more serious if it starts earlier (16-18 years).
Don’t worry, I have solutions for you. Although it is impossible to completely stop hair loss, it is possible to control its progression and slow it down. So, instead of waiting to see what life has in store for us, let’s act early and intervene before the quality of your hair degenerates.

